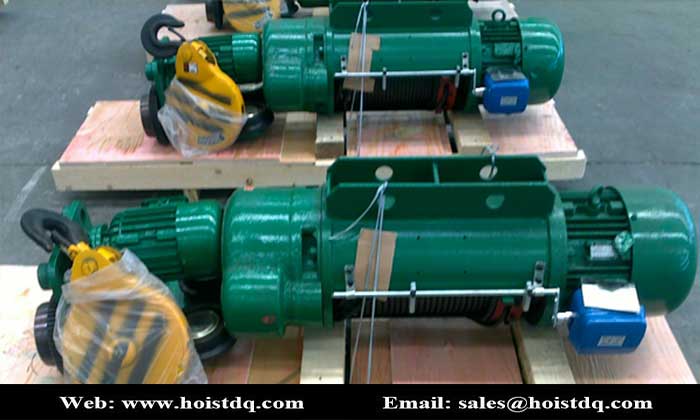
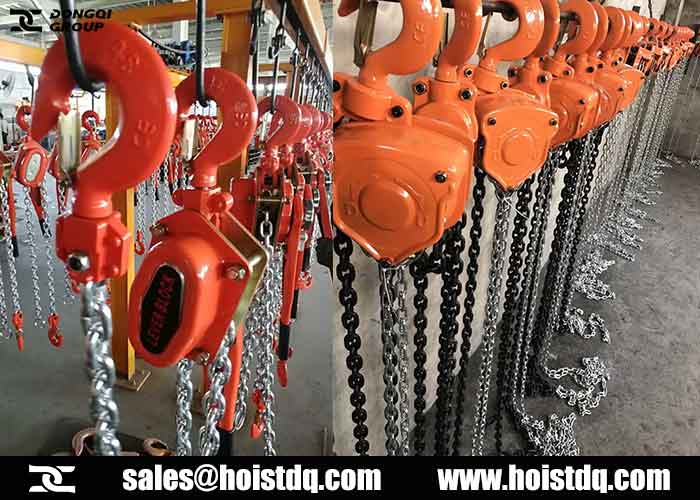
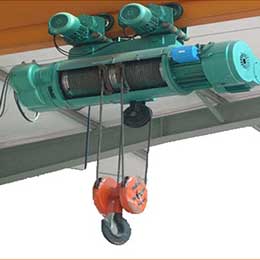
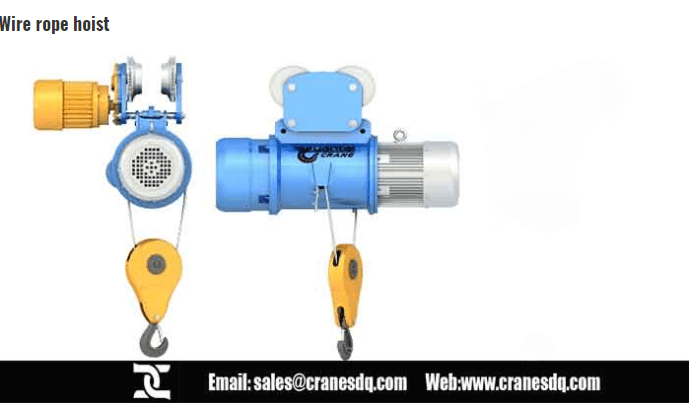
What is electric hoist?
An electric hoist is designed for lifting, lowering, and horizontally moving loads within its rated capacity. It is commonly used in industrial, construction, and warehouse settings. Key components typically include:
- Electric motor: Powers the hoist’s lifting mechanism.
- Lifting medium: A chain or wire rope to handle loads.
- Hooks: For attaching loads securely.
- Control system: Operated via pendant, remote controls.
- Safety features: Overload protection, emergency stop, and thermal safeguards to prevent overheating.
Applications: Widely used in construction, manufacturing, warehouses, and automotive industries for tasks like material handling, assembly, and equipment maintenance.
Electric Hoist Types
Electric hoists vary based on design, power source, and mounting:









By Lifting Medium:
- Chain Hoists: Use a durable alloy chain; ideal for lighter loads and portable applications.
- Wire Rope Hoists: Utilize steel cables for heavy-duty tasks and higher lifting heights.
By Power Supply:
- Single-Phase: For standard electrical outlets (common in small workshops).
- Three-Phase: For industrial settings with higher power demands.
By Mounting Style:
- Pendant-Controlled: Operated via a hanging control panel.
- Remote-Controlled: Wireless operation for flexibility.
- Trolley-Mounted: Moves along a beam for horizontal transport.
- Fixed Mounts: Permanently installed for specific workflows.
Safety Precautions
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Wear gloves, safety glasses, steel-toe boots, and a hard hat.
- Avoid loose clothing or jewelry that could snag.
Work Area Safety:
- Ensure the area is clear of personnel and obstacles.
- Verify adequate lighting and ventilation.
- Do not operate in explosive atmospheres unless the hoist is rated for it.
Load Limits:
- Never exceed the hoist’s rated capacity (listed on the nameplate).
- Account for sling angles and load center of gravity.
Power Supply:
- Confirm voltage matches the hoist requirements.
- Inspect cables and plugs for damage before use.
Prohibited Actions:
- Do not lift people or unstable/unsecured loads.
- Never leave a suspended load unattended.
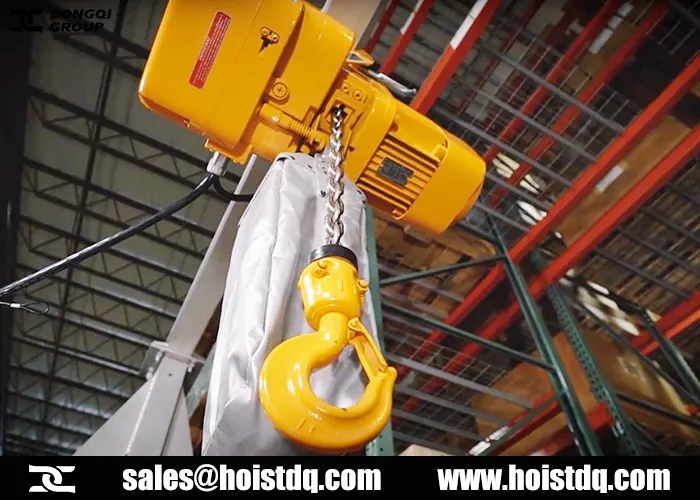

Pre-Operation Inspection
Hoist Components:
- Check chains/cables for wear, rust, or deformation.
- Inspect hooks for cracks or deformation; ensure safety latches function.
- Test controls (up/down, left/right) for responsiveness.
- Examine brakes and limit switches.
Load Rigging:
- Verify slings/straps are undamaged and rated for the load.
- Ensure the load is balanced and secured.
Environment:
- Confirm no environmental hazards (e.g., chemicals, high humidity).
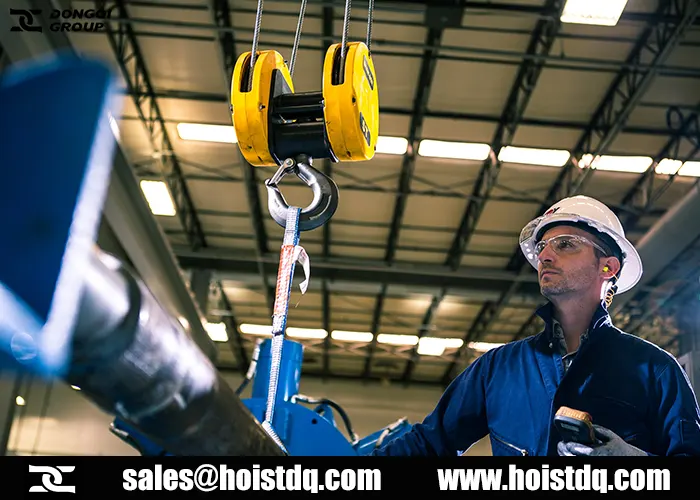

Operating Instructions
- Step 1: Prepare the Work Area. Clear debris and ensure stable footing. Alert nearby personnel before starting.
- Step 2: Attach the Load. Use appropriate rigging (e.g., shackles, slings). Center the load under the hoist to prevent swinging.
- Step 3: Lift the Load. Press the “UP” button to lift it slowly. Pause 0.5-1ft off the ground to test stability and balance.
- Step 4: Move the Load. Move smoothly; avoid sudden stops. Keep the load low and controlled to minimize swing.
- Step 5: Lower the Load. Lower gently to the designated spot. Release tension from slings before disconnecting.

Emergency Procedures
- Power Failure: Secure the area; use manual override (if trained) to lower the load.
- Mechanical Failure: Activate emergency stop. Do not attempt repairs while loaded.
- Overload: Stop immediately. Use a secondary hoist or redistribute weight.
Maintenance and Storage
- Daily/Weekly Inspections: Check for wear, corrosion, or deformation in chains/wires.
- Monthly Brake Tests: Ensure brakes hold loads securely.
- Lubrication: Apply approved grease to chains, wires, and moving parts.
- Electrical Checks: Inspect cables and connections for damage.
- Record-Keeping: Document all maintenance and inspections.
- Storage: Keep it in a dry, covered area; disconnect the power.
Contact DQCRANES for Help!
- Troubleshooting and technical support.
- Replacement parts or warranty claims.
- Operator training programs.
- Custom hoist solutions.
Note: Always reference your hoist’s model number when requesting assistance.